1 (Exercise 12) Find the maximum and minimum of f(x;y;z) = x4 y4 z4 subject to the constraint x 2y2 z = 1 Solution We have ∇f(x;y;z) = 4x3;4y3;4z3 = 2 x;2 y;2 z = ∇g(x;y;z) Case 1 If all of x;y;z ̸= 0, we can divide 4x3 = 2 x, 4y3 = 2 y, 4z3 = 2 z by 4x;4y;Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeLet {eq}f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 {/eq} and let S be the level surface defined by f(x,y,z) = 4 (a) Find an equation for the plane tangent to S at {eq}P_{0}(1,1,2)
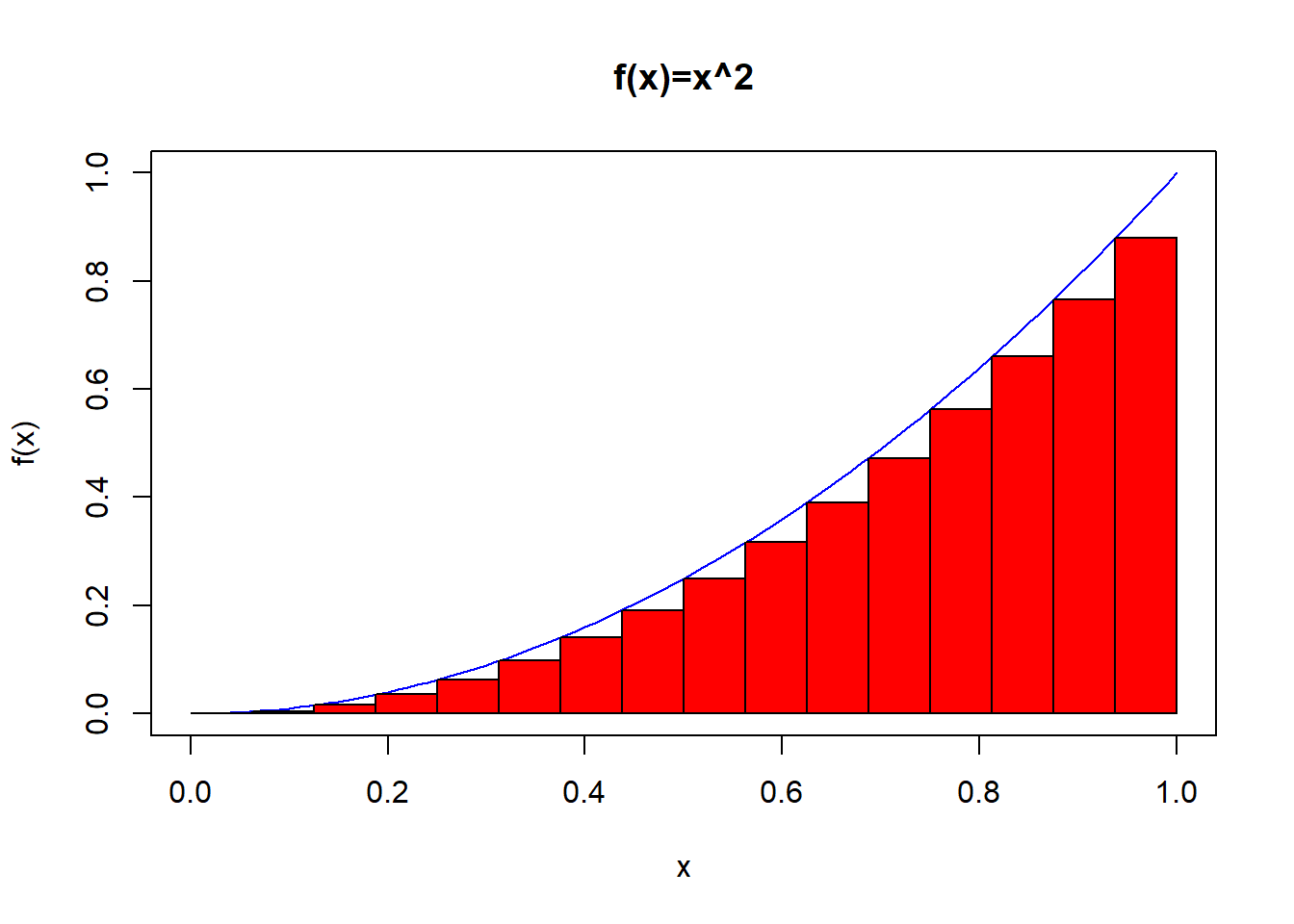
Triple Integrals In Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates
F(x y z)=x^2+y^2+z^2
F(x y z)=x^2+y^2+z^2-Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyAnswer to Find the vector field grad f for f = x^2 y z z^2 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework


Chapter 7 Functions Of Two Variables Calculus And Analysis
Surface integrals Find the area of the portion of the cone x^2y^2=z^2 above the xy plane and inside the cylinder x^2y^2=axQuestion Let S Be The Sphere X^2 Y^2 Z^2 = 4 Oriented By Outward Normals And Let F(x,y,z = Zk) Use The Divergence Theorem To Evaluate Integral Integral F Middot N DS It Equals A 16 Pi/3 B 32 Pi/3 C 64 Pi/3 D 128 Pi/3 Let W Be The Region Bounded By The Cylinder X^2 Y^2 = 4, Between Z = 0, And Z = 32 share Report Save Continue this thread
1 Verified Answer View AnswerY Simplify —— x 2 Equation at the end of step 1 y (((((x 2)(y 2))(z 2))(2x•——))y 2)z 2)2xz x 2 Step 2 Rewriting the whole as an Equivalent Fraction 21 Subtracting a fraction from a whole Rewrite the whole as a fraction using x as the denominatorYou can quite easily reduce this system to a single cubic equation However, solving a general cubic equation is not simple To reduce the system, you should read up on Newton's identities What you call a, b, c they call p1, p2, p3 The Cubic fun
Let f(x) be a differentiable function satisfying f (x y) = f (x) f (y) ∀ x, y ∈ R and f (0) = 1 then x → 0 lim x 3 f (sin x) 2 f (t a n 2 x) − 2 f (s i n 2 x) equals to?Expand (xyz)^2 Rewrite as Expand by multiplying each term in the first expression by each term in the second expression Simplify each term Tap for more steps Multiply by Rewrite using the commutative property of multiplication Rewrite using the commutative property of multiplicationCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and
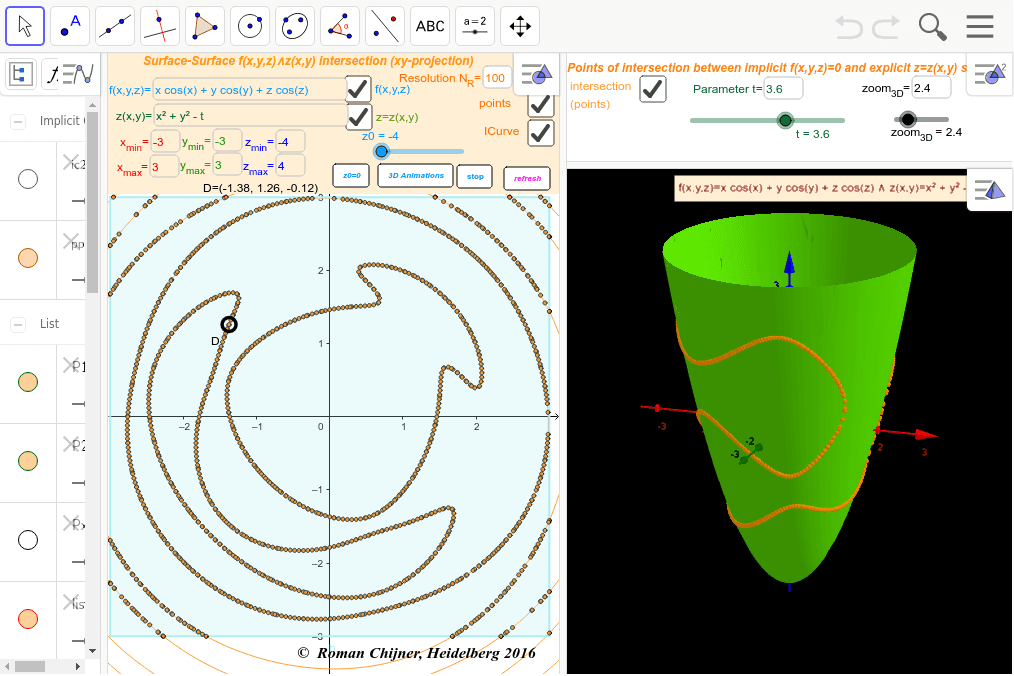


Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra



Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu
Aug 30, 15 · (delw)/(delx) = x/sqrt(x^2 y^2 z^2) (delw)/(dely) = y/sqrt(x^2 y^2 z^2) (delw)/(delz) = z/sqrt(x^2 y^2 z^2) Since you're dealing with a multivariable function, you must treat x, y, and z as independent variables and calculate the partial derivative of w, your dependent variable, with respect to x, y, and z When you differentiate with respect to x, you treat y and zProve that f(x, y, z) = x^2y^2z^22x2y2z3 is a continuous function from R^3 to R (ie show that f^{1} ((a, b)) is open in R^3 ) Prove that f (x, y, z) = x 2 y 2 z 2 2 x 2 y 2 z 3 is a continuous function from R 3 to R18 f(x, y, z) = z;


Examples Wednesday Feb 19


Sketching Surfaces In 3d
Check out a sample textbook solution See solution arrow_back Chapter 148, Problem 17E Chapter 148, Problem 19E arrow_forward Want to see this answer and more?In order to evaluate the triple integral {eq}f(x, y, z) = z(x^2 y^2 z^2)^{3/2} {/eq} over the part of the ball {eq}x^2 y^2 z^2 \le 49 {/eq} defined by {eq}z \geq 35 {/eq}Letf (x,y,z) = x^2y^2z^2 Calculate the gradient of f Calculate ∫_C (F dr) where F (x,y,z)= (x,y,z) and C is the curve parametrized by r (t)= (3cos^3 (t), 2sin^5 (t), 2cos^13 (t) for 2π≤t≤3π



Plotting Contours Plot For F X Y Z C Mathematica Stack Exchange



Find The Extreme Values Of The Function F X Y Z X 2 2y 2 Subject To The Constraint X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Homeworklib
And 4z to get x2 = y2 = z2 = 2 Since x2 y2 z2 = 3 2 = 1, we get = 2 3 and thus each of x;y;z is p1 3Contact Pro Premium Expert Support »View COM 180 note sckjvtilpwxwlpypdf from COM 180 at Georgetown Day School Step1 we have to Show that F(x,y,z)=xiyjzk f(x,y,z)= lnf=1/2lnx^(2)y^(2)z^(2) (x)/(x^(2)y^(2)z^(2)


Triple Integrals In Cylindrical And Spherical Coordinates



Level Surfaces In Matlab
Minimize the function f(x, y, z)=x^{2}y^{2}z^{2} subject to the constraints x2 y3 z=6 and x3 y9 z=9 Video Transcript So the question is gonna look a little bit different We instead of having one constraints, we're gonna find extreme valueA) it amounts to solving in Z x 2 y 2 = 3 z 2 You have that x 2 y 2 = 0 (m o d 3) → x = y = 0 (m o d 3), and you get back the original one using descending method, and this proves x = y = z = 0Jun 17, 17 · Despite the fact that the same variables appear in every term, this expression does not factorize into one term There is no common factor, and no common bracket EAch term can be factored by differemce of squares xy(x^2y^2) yz(y^2z^2) zx(z^2x^2) =xy(xy)(xy) yz(yz)(yz) zx(zx)(zx) The only other option would be to multiply out the brackets and try a



Describe The Level Surfaces Of The Function F X Y Z X 2 3y 2 5z 2 Study Com


C5
The same idea applies, the term under the square root can't be negative, ie 25x 2y 2z 2 >=0 1 share Report Save level 2 5 years ago So 25>(x,y,z)>0 as xyz can't be less than zero, and if they're greater than 25 than the entire function becomes less than 0 Would that be a suitable answer?When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;Equations Tiger Algebra gives you not only the answers, but also the complete step by step method for solving your equations x^22xyy^2z^2/(x^22xyy^2z^2)o so



Calculus Iii Divergence Linear Algebra



Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu
S is defined as a sphere However, when I type "S f(x,y,z) = 1" into the input bar, nothing is graphed and the algebra window shows S as an undefined Implicit CurveWe think you wrote (2xy3z2xy^2z/(x^2yy^2zxz^2))*x^2yy^2zxz^2 This deals with adding, subtracting and finding the least common multipleWolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and capabilities to the broadest possible range of people—spanning all professions and education levels



How Do I Reproduce This Heart Shaped Mesh In Matlab Stack Overflow



Answered 14 F X Y Z X Y 4z X Y Bartleby
Verify Euler's theorem for f (x, y) = x 2 y 2 1 View solution If f ( x , y , z ) = a 2 x 2 b 2 y 2 c 2 z 2 − 1 , then Σ x ∂ x ∂ f is equal to4 and having density f x y z p x 2 y 2 z 2 The cone z 2 x 2 y 2 z 0 in from MATH 3 at The City College of New York, CUNYThe idea is that since xyz is cubic, it will be larger than x 2 y 2 z 2 unless one number is much larger than the others But if that's the case, we can always replace the largest number with a smaller one (until x,y,z form an acute triangle)



Consider Minimizing And Or Maximizing A Function Z F X Y Subject To A Constraint G X Y C Y Z X Z F X Y Parametrize The Curve Defined By G X Y Ppt Download



1 Given F X Y Z As Z 2 Y Find A The Partial Derivative F X Y Homeworklib
Jun 22, 19 · x^2y^2z^2=xyyzzx eq(1) Identity is x^3y^3z^3 3xyz=(xyz)(x^2y^2z^2xyyzzx) x^3y^3z^3 3xyz =(xyz)(xyyzzxxyyzzx) (acc to eq1) Therefore , x^3y^3z^3 3xyz = 0 So, x^3y^3z^3= 3xyz Answer read moreFactors of x2y2z2xyyzzx, Factors of x^2y^2z^2xyyzzx, Factors of a2b2c2abbcca,Factors of a^2b^2c^2abbcca, Factors of p2q2r2pqqrpr(a)Series x^2 y^2 z^2 f(x, y, z) show histogram of image image of x^2 y^2 z^2 f(x, y, z) Have a question about using WolframAlpha?
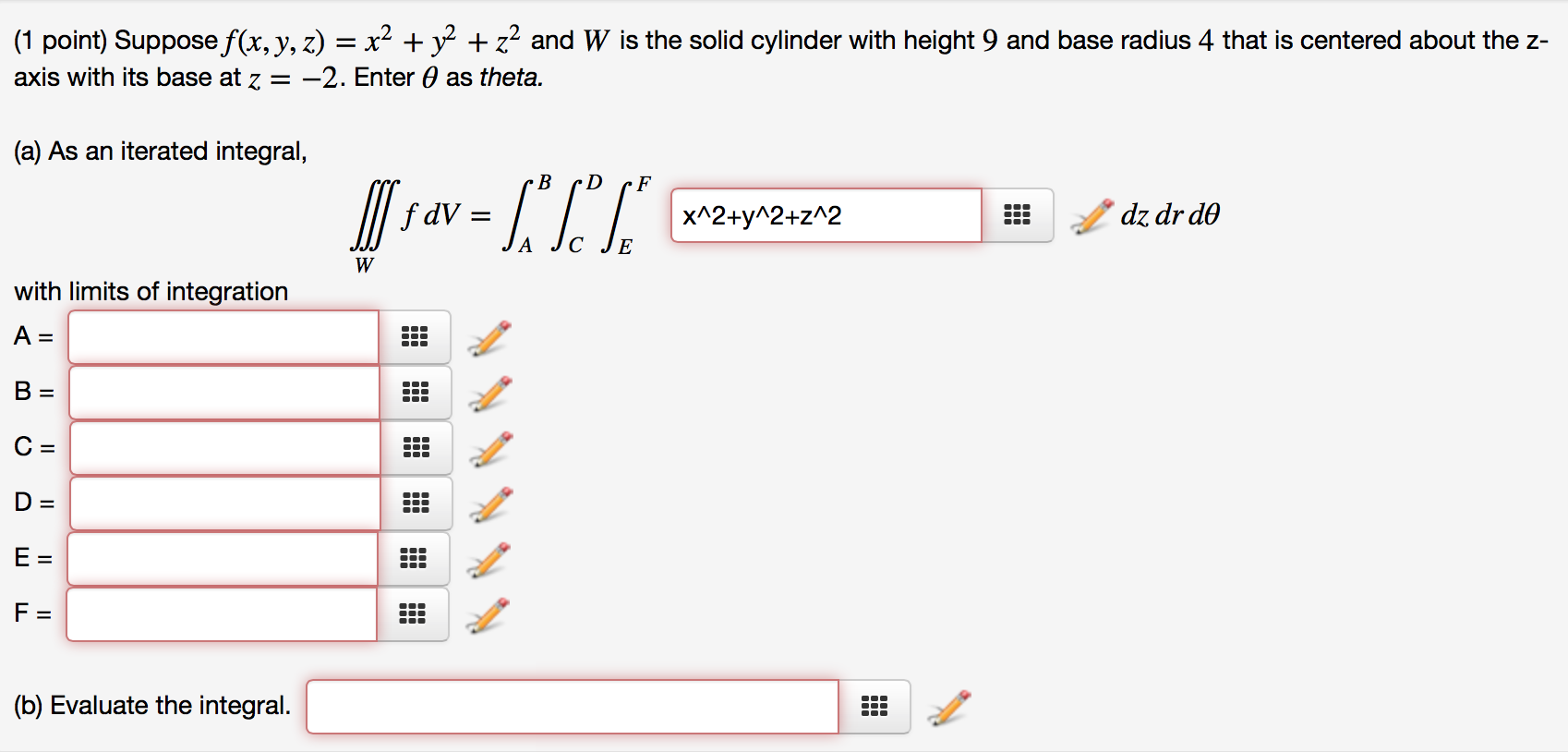


Solved Suppose F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 And W Is The Solid Cy Chegg Com


Surfaces Part 2
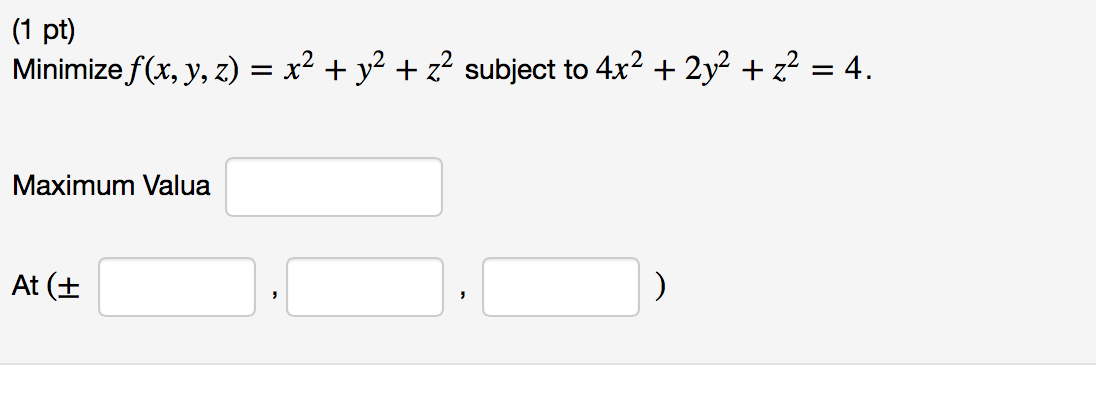
Let f(x, y, z)=e^{x^{2}y^{2}z^{2}}=e^{r^{2}}, with r as in Exercise 31 Compute \nabla f directly and using Eq (9)Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If x^2 = y z, y^2 = z x, z^2 = x y , then the value of 1x 1 1y 1 1z 1 isMinimize f(x, y, z) = x^2 y^2 z^2 subject to 4x^2 2y^2 z^2 = 4 Maximum Valua At (,,) (1 pt) Find the coordinates of the point (x, y, z) on the plane z = 2 x 2 y 3 which is closest to the origin x = 2 y = z = Get more help from Chegg Solve it
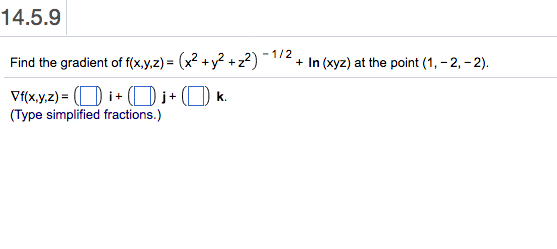


Solved Find The Gradient Of F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Chegg Com



Solved Let F X Y Z 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Find The Domai Chegg Com
May 21, 10 · Construct the function of 5 variables F(x,y,z,a,b) = x^2y^2z^2 a(x6z5)b*(xy10) Compute the partial derivatives of F with respect to x, y, z, a, b Fx= 2xab Fy= 2yb Fz= 2z6a Fa= x6z5 Fb= xy10 Set all these five partial derivatives to 0 and solve the resulting system From the first x= (ab)/2 From the second y =b/2 From the thirdホーム>>カテゴリー別分類>>数と式>>整式:因数分解の公式 (xyz)(x^2y^2z^2xyyzzx) 最終更新日: 14年9月9日 ページCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history



S Consists Of The Paraboloid Y X 2 Z 2 0 Y 1 And The Disk X 2 Z 2 1 Youtube
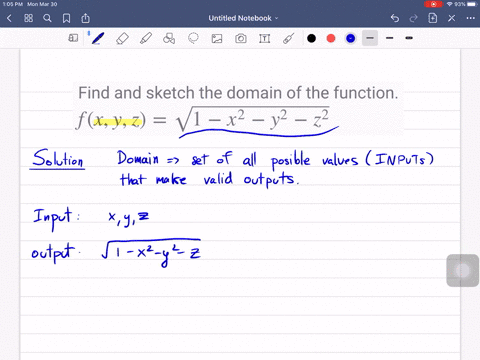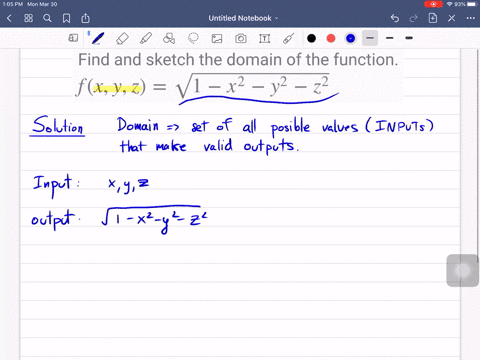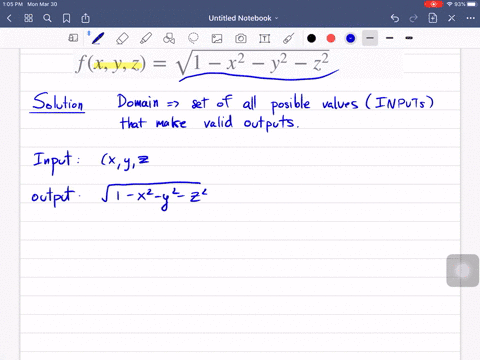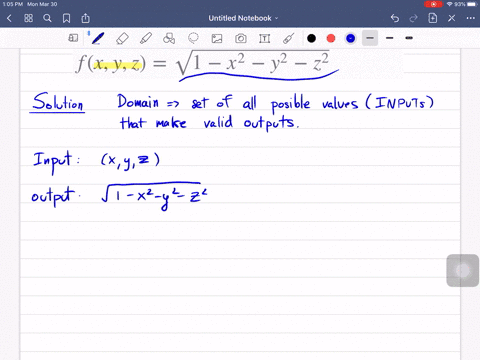


Solved Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function
Using the theory of elliptic curves, we study the nontrivial rational (parametric) solutions of the Diophantine equations $z^2=f(x)^2 \\pm f(y)^2$ for some simpleApr 28, 17 · Let $x,y,z\\in \\mathbb{Z}$ Find all naturals $n$ such that the equation $x^2y^2z^2=n(xyyzzx)$ has nontrivial solution(s) (ie other than $(0,0,0)$), or proveNov 24, 19 · Verify Stokes theorem for F =(y^2 x^2 x^2)i (z^2 x^2 y^2)j (x^2 y^2 z^2)k over the portion of the surface x^2 y^2 2ax az = 0 While evaluating the integral we get hard to evaluate integrals What can we do to simplify this?



Lagrange Multipliers By Rohit Venkat Ppt Video Online Download



Multiplicadores De Lagrange Maxima And Minima Space
Math Chain rule Consider the function f (x, y, z) = x^2yz^2 defined on the sphere x^2 y^2 z^2 = 9 iX 2 y 2 = z 2, x y z = 24 check_circle Expert Solution Want to see the full answer?



181calculus 344 F X Y Z X 2y 2z X2 Y2 Z 2 9 A Maximum 9at 1 2 2 Minimum 9at 1 2 2 B Maximum 1at 1 2 2 Minimum 1at 1 2 2 C Course Hero



Solutions To Assignment 3



Chapter 7 Functions Of Two Variables Calculus And Analysis



Oneclass Use Lagrange Multipliers To Find The Maximum And Minimum Values Of F X Y Z X2 8y 10z2 Subj



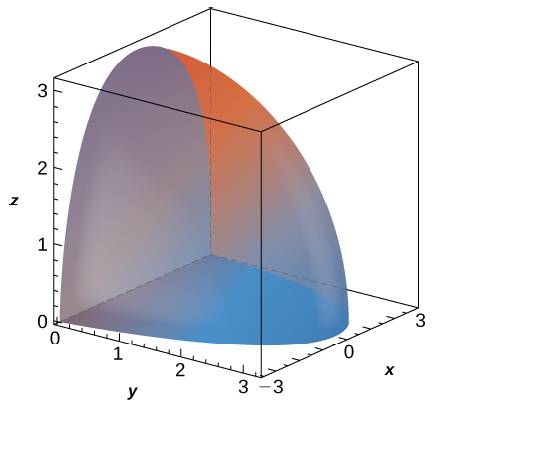
Find The Average Value Of F X Y Z Xyz Over The Region X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Less Than Or Equal To 1 Study Com


Matematicas Animadas


In Triangle Xyz Z2 X2 Y2 Triangle Xyz Has Sides X Qy Z Opposite To The Corresponding Vertices Brainly Com



32 Approximation Of Eg6 Shrek F X Y Z X 4 Y 4 Z 4 4 X 2 Download Scientific Diagram
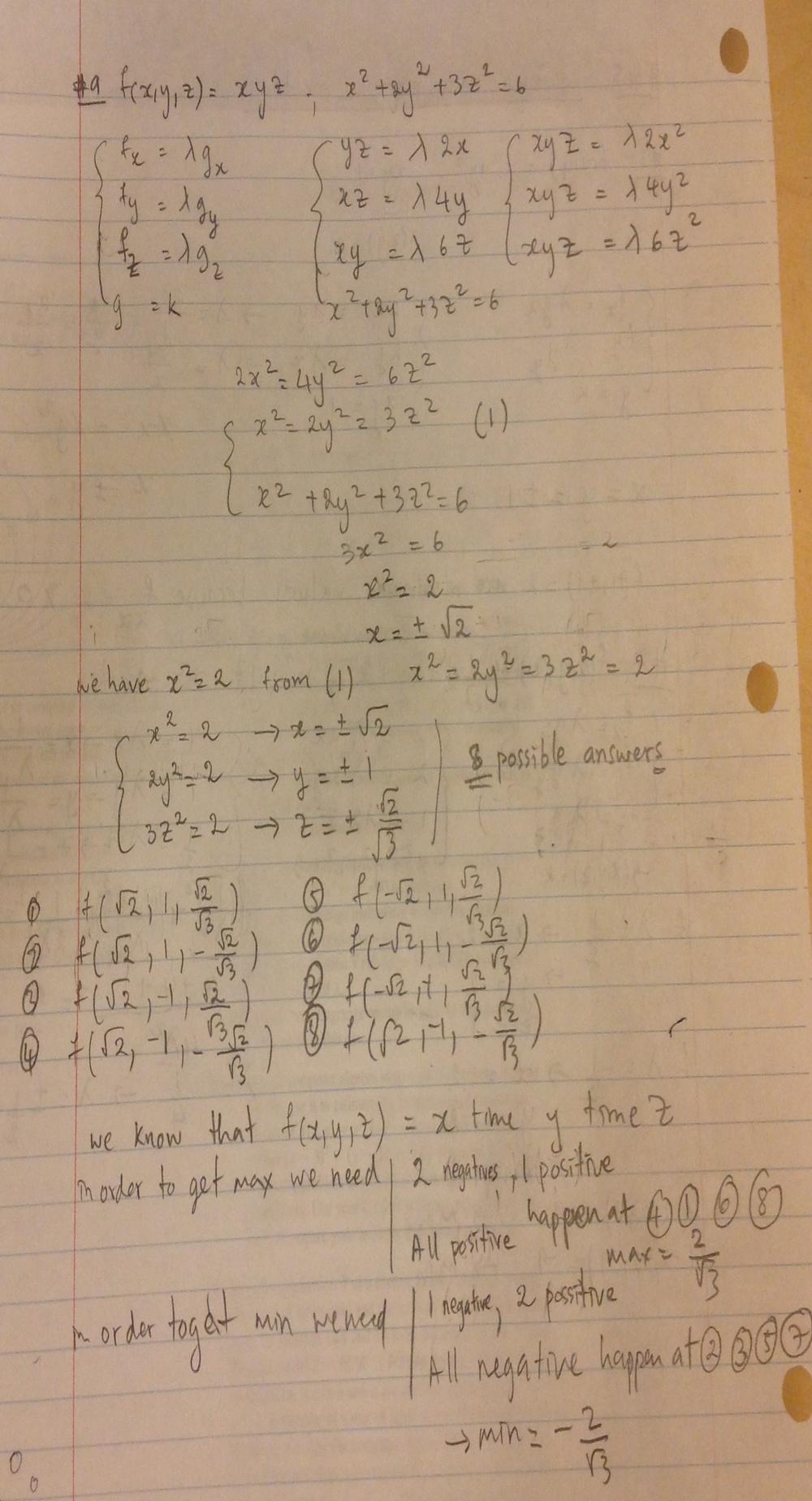


Use Lagrange Multipliers To Find The Maximum And Minimum Values Of The Function Subject To The Given Constraint F X Y Z Xyz X 2 2y 2 3z 2 6 Homework Help And Answers Slader



Compute The Divergence Of The Vector Field F X Y Z Ln X 2 Y 2 I Math Videos F X Computer


Find The Maximum Value Of X Y Z When Ax By Cz P Quora



Solve The Equation X 2p 2 Y 2q 2 Z 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
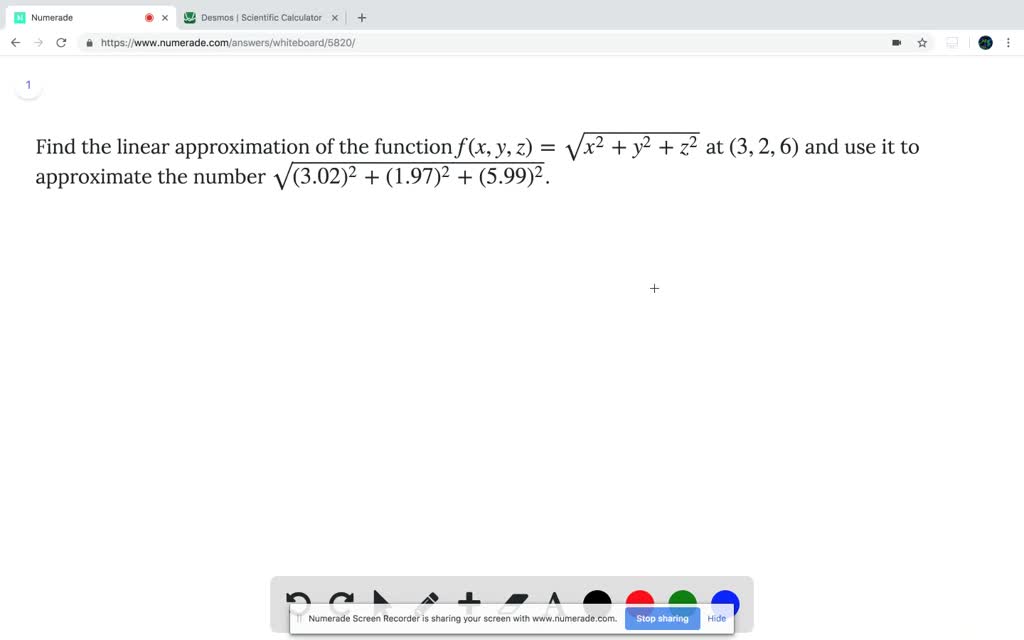


Solved Find The Linear Approximation Of The Funct



2a Ex7 1314with Sol Tutorial Work With Full Detailed Solutions Studocu
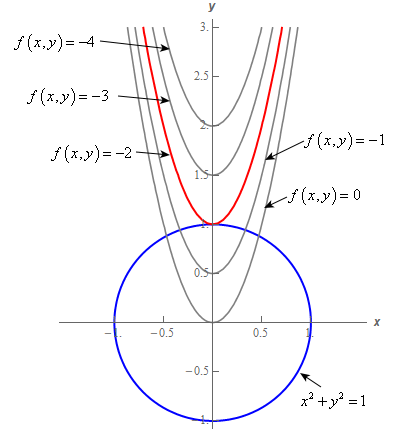


Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers


Sketching Surfaces In 3d
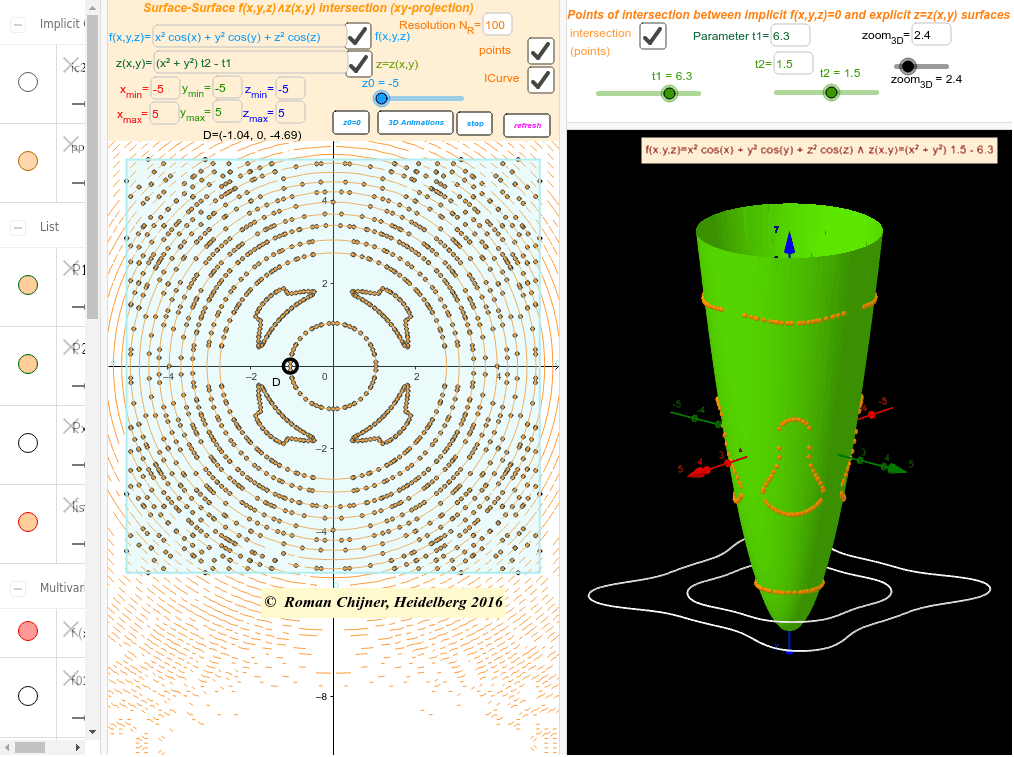


Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra


270 F X Y Z 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 B X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 9 Y 0 Z 0 Bartleby
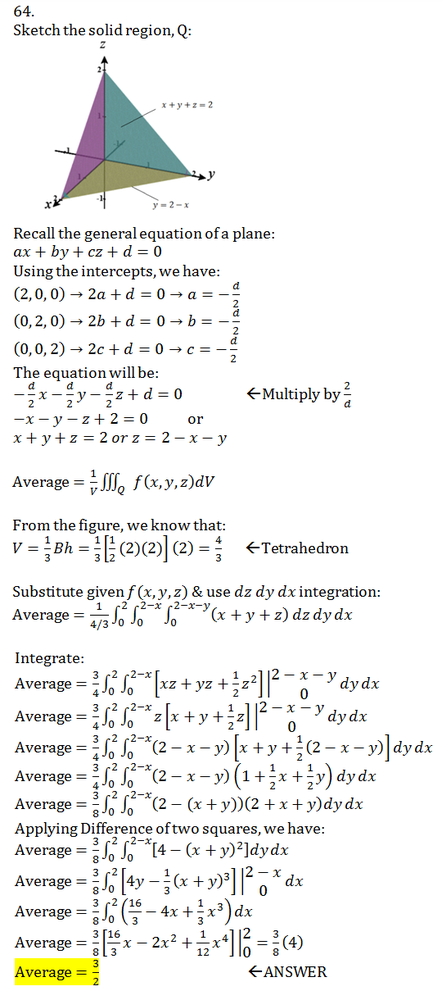


Find The Average Value Of The Function Over The Given Solid F X Y Z Xyz Over The Cube In The First Octant Bounded By The Coordinate Planes And The Planes X
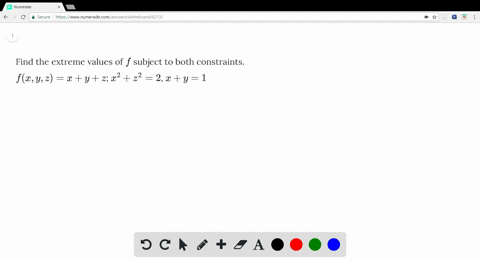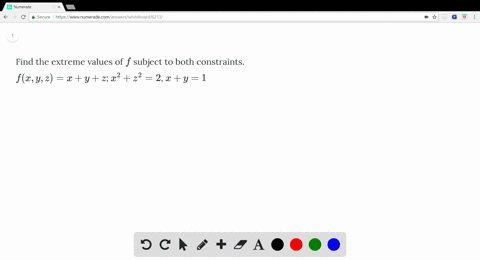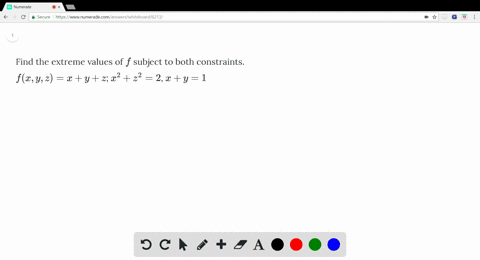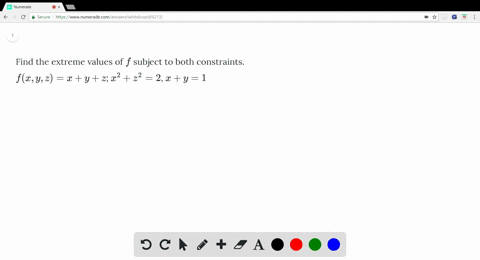


Solved Find The Minimum Value Of F X Y Z X 2



7 A If F Xyz X2yy2xz2 Find V See How To Solve It At Qanda


Matematicas Animadas



Section 12 8 Lagrange Multipliers



The Equation To Sphere Passing Throrugh Origin And The Points 1
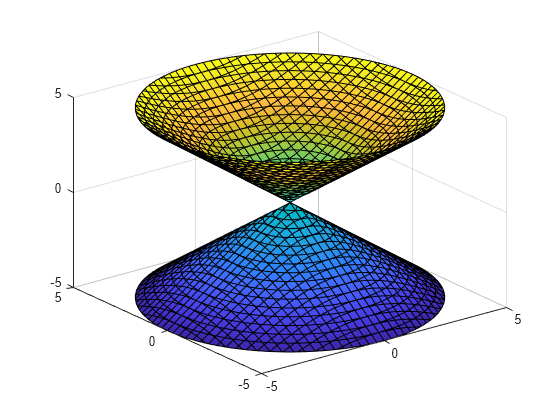


Plot 3 D Implicit Function Matlab Fimplicit3



Matlab Tutorial



F X Y Z X 2 1 2 Y 2 1 2 Z 2 1 2 3 2 Download Scientific Diagram


How To Determine The Extreme Values Of The Function Math F X Y Z X 2y 2z Math For Condition Math X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Math Quora


Find The Gradient Vector Field Of F F X Y Z 10 X2 Y2 Z2


Lagrange Multipliers Maximum Of F X Y Z Xyz Subject To X Y Z 3 0 Youtube



Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download


Lagrange Multipliers Minimum Of F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Subject To X Y Z 9 0 Youtube


Solved Minimize F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Subject To 4 Chegg Com



Get Answer Show Transcribed Image Text Consider F And C Below F X Y Z Transtutors


Solved Find The Maximum And Minimum Values Attained By F X Y Z 2 Xyz On The Unit Ball X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Course Hero


Level Surfaces Nb



Extremes Of F X Y Z X 1 2y 2 Z 1 2 With X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Leq 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange


Curl Of A Vector Field Web Formulas
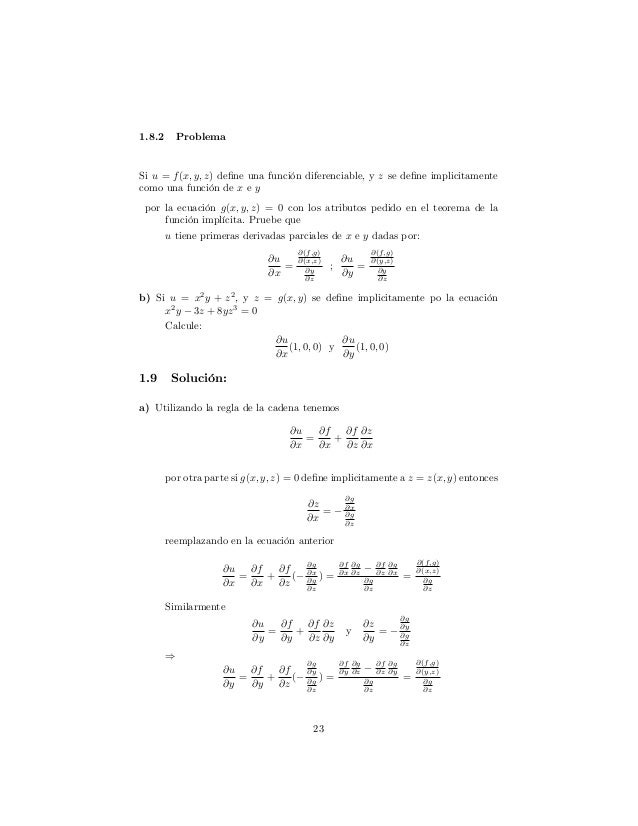


Problemas Resueltos 1oct Max
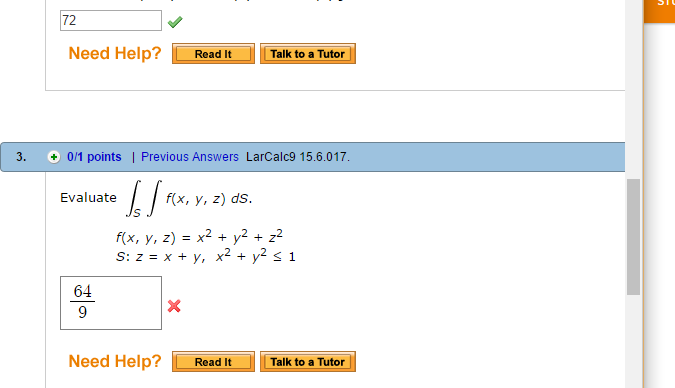


Solved Evaluate S F X Y Z Ds F X Y Z X2 Y2 Z Chegg Com
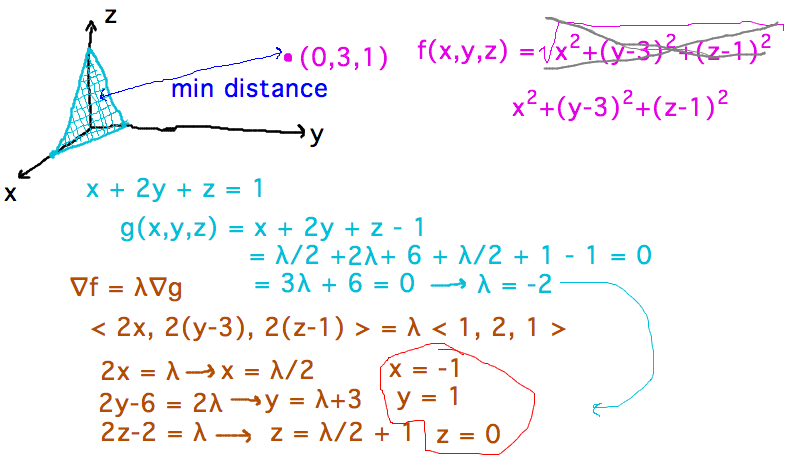


Geneseo Math 223 03 Lagrange Multipliers
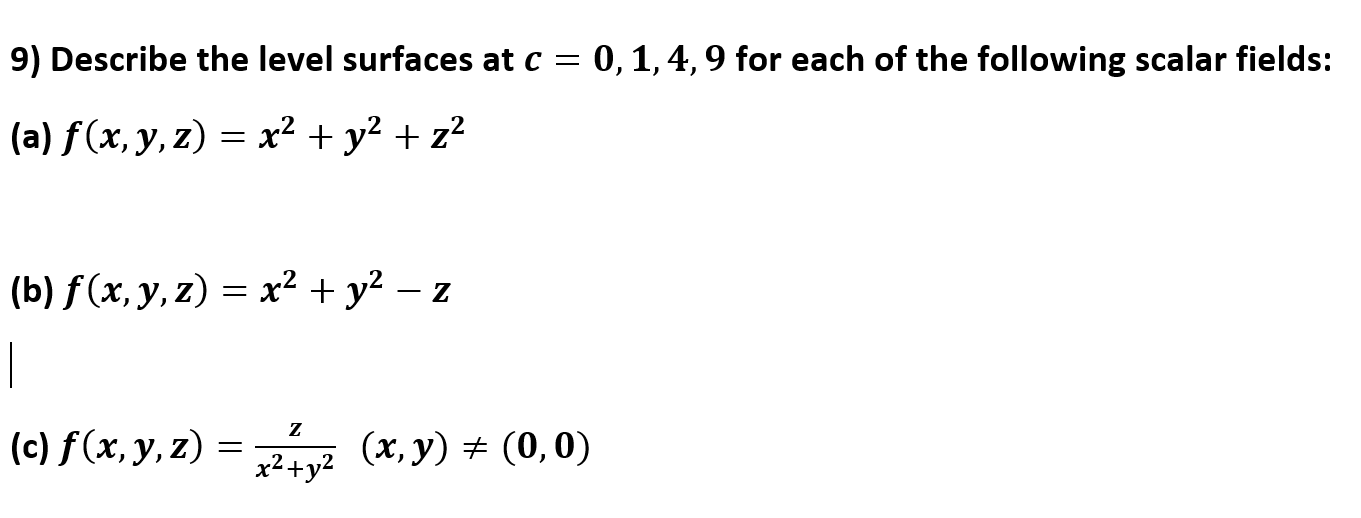


Answered 9 Describe The Level Surfaces At C Bartleby



Make 2x 2 Y 2 Z 2 X 2 2y 2 Z 2 X 2 Y 2 2z 2 Squares Fun With Num3ers



Solved 2 A Find The Gradient Field Of The Functions Chegg Com
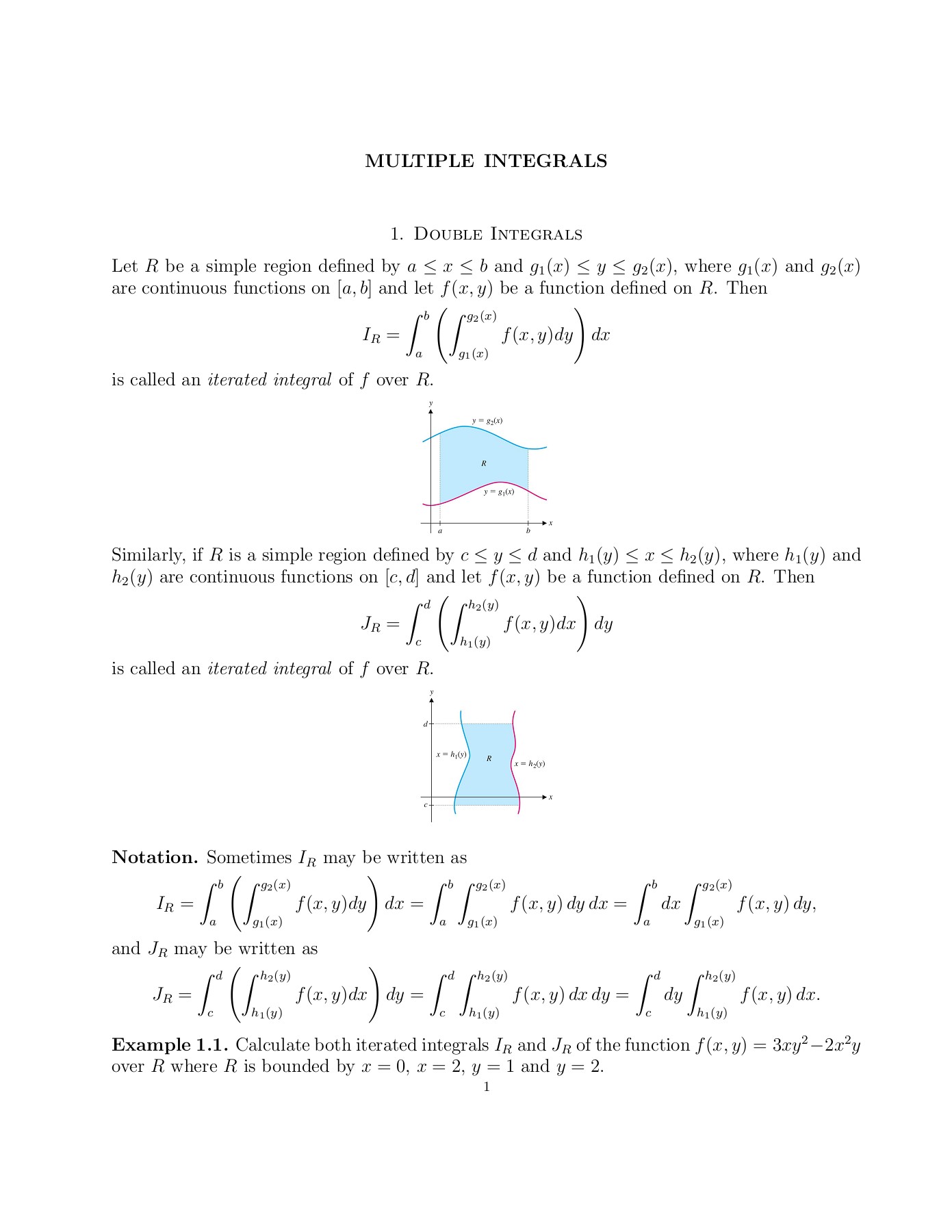


1 Double Integrals Cankaya Universitesi Flip Ebook Pages 1 16 Anyflip Anyflip



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿